Hello, this is MONITORAPP.
Today, we will briefly share about the various Load Balancers provided by
AWS, and in particular, dive deeper into the details of GWLB.
AWS’s various Load Balancer services
AWS offers a variety of load balancer services to help distribute traffic
and improve reliability and scalability.
The main types of load balancers are as follow:
Classic Load Balancer (CLB)
The most basic and traditional load balancer that distributes HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP traffic,
and is used to distribute traditional web applications and network traffic.
Network Load Balancer (NLB)
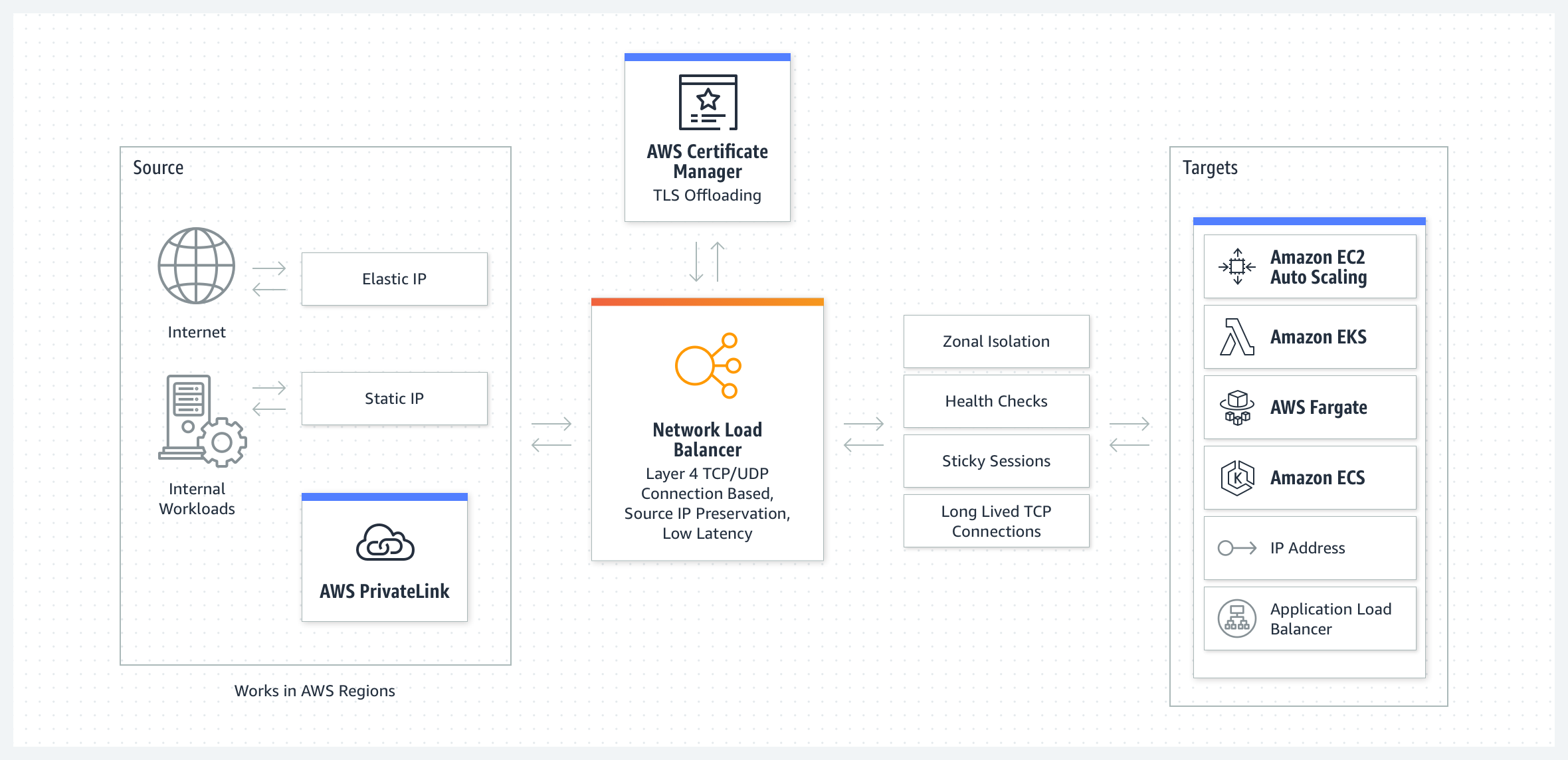
A load balancer that operates at OSI layer 4 and distributes TCP and UDP traffic,
featuring high performance and low cost.
It is mainly suitable for applications that require fast performance based on TCP and UDP.
Application Load Balancer (ALB)
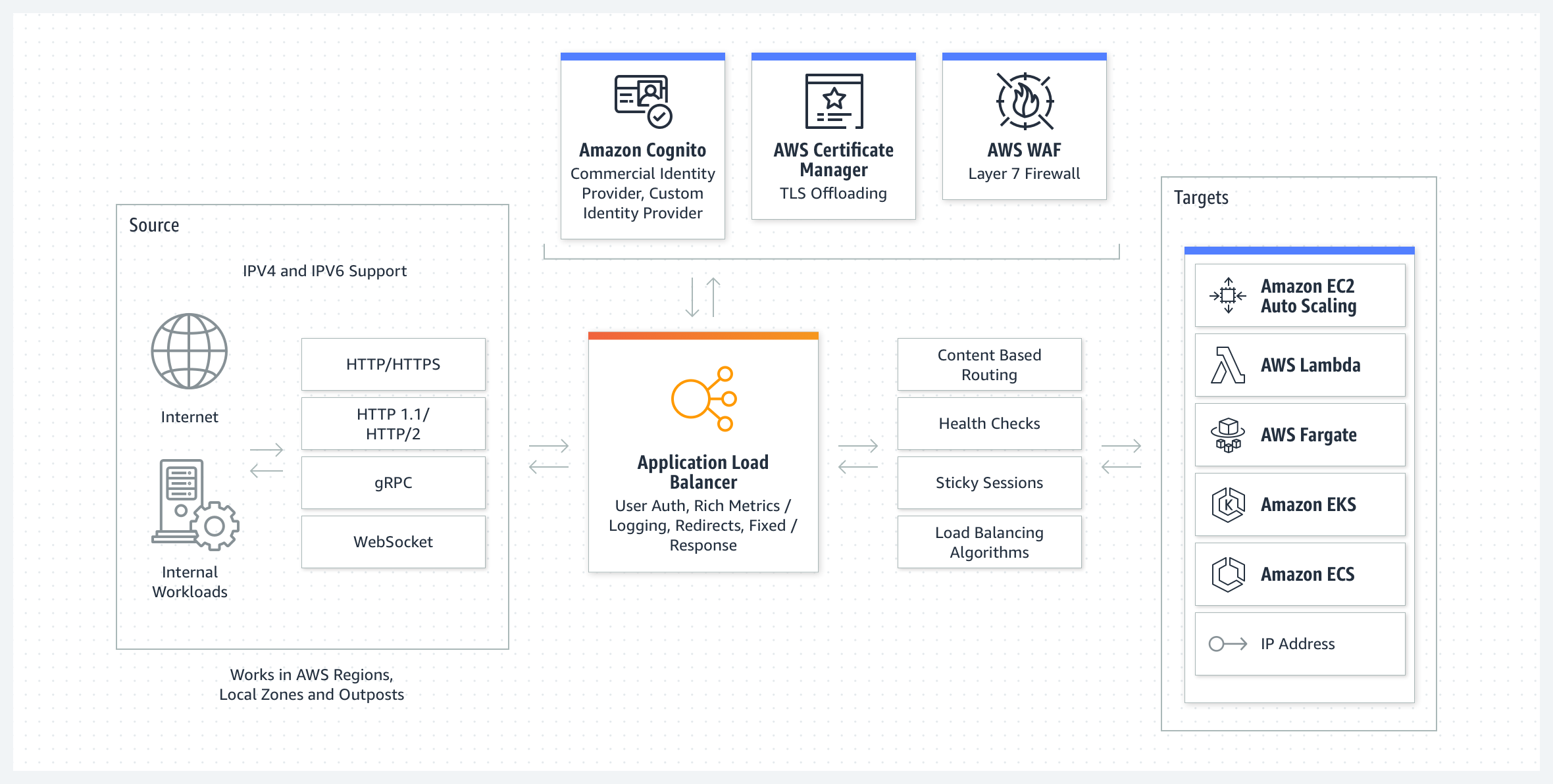
A load balancer operating at OSI layer 7 based on HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
ALB provides routing and specific application-level functions,
making it suitable for modern web applications and microservices architectures.
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
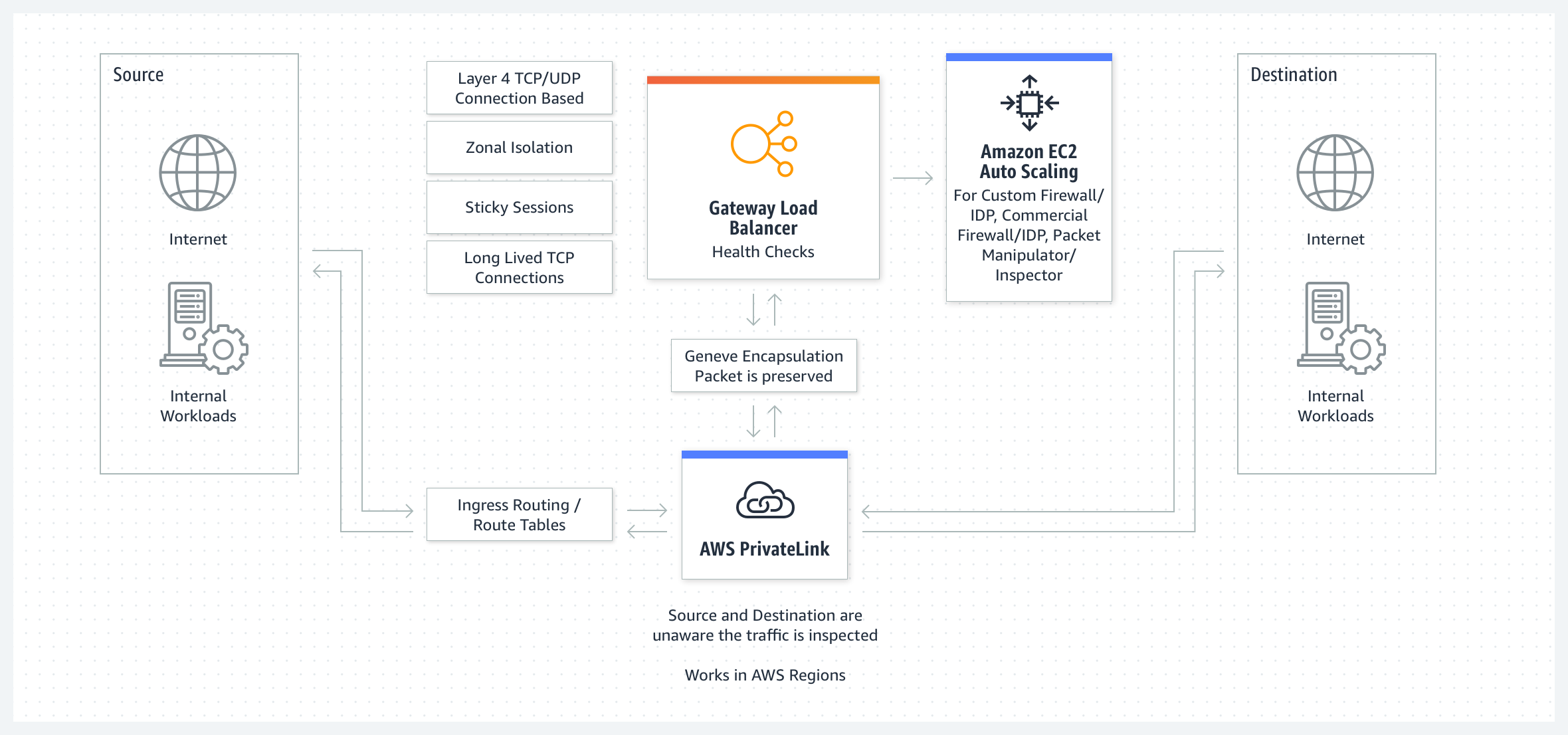
GWLB operates at OSI layer 3 and handles IP traffic.
It can be configured across multiple Availability Zones,
making it suitable for large-scale IP-based workloads and serving as a
gateway for VPN, Direct Connect, etc.
What is Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)?
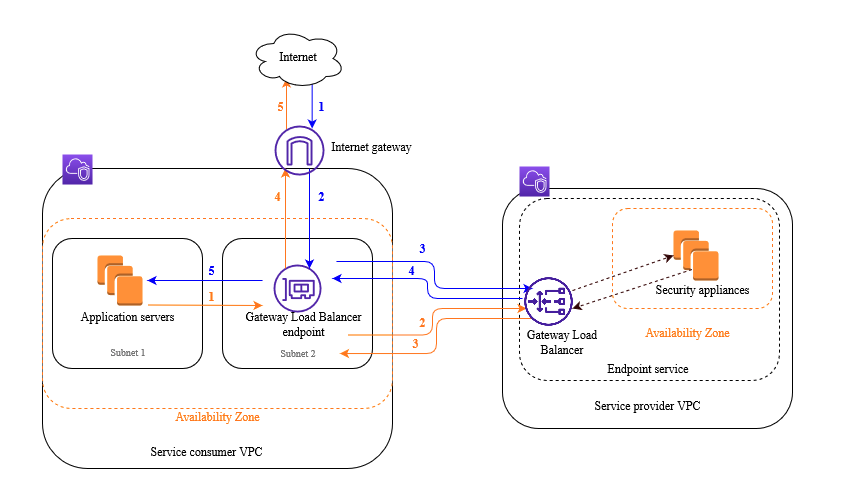
AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a load balancer that operates at OSI layer 3 ,
and can effectively manage IP traffic and distribute large-scale workloads
across multiple Availability Zones.
In particular, GWLB addresses the need for security solutions
to track clients’ IP addresses by providing the ability to maintain the
client’s actual IP address.
Layer 3 Load Balancing
GWLB distributes traffic at the IP address and port level, which means load balancing at OSI layer 3.
High Availability & Scalability
GWLB is scalable across multiple Availability Zones and provides high availability to improve application reliability.
The Integration of VPN and Direct Connect
GWLB, integrated with VPN and AWS Direct Connect, provides a scalable network architecture in hybrid cloud environments.
Security and Monitoring
GWLB, integrated with AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF), AWS Shield, VPC Flow Logs, etc., can enhance security and monitoring.
Role of Encapsulation Protocols, including GENEVE
There are various encapsulation protocols in the network, including the GENEVE protocol.
Encapsulation is an essential concept in network communications and
plays an important role in strengthening security and interoperability by
supporting the safe transmission of data
and efficient management of the network.
Data Encapsulation
Encapsulation encapsulates data into packets to ensure secure transmission.
This ensures that data integrity is maintained and that there is no manipulative intervention.
Enhanced Security
In terms of security, encapsulation enhances the security of communications
on a network by ensuring secure transmission of data.
Encapsulation plays an important role, especially in VPN (Virtual Private Network).
Integration of Diverse Network Environments
Encapsulation is used to integrate different network environments into one.
It also supports interoperability between various networks by integrating
various protocols and technologies.
Client Identification
A common encapsulation protocol preserves the client's actual IP address,
which is used to identify the client in security solutions.
This helps with client management and security policy enforcement.
Classification
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
GRE is responsible for encapsulating IP packets and tunneling them to another network.
It supports communication between various networks and is often utilized in
virtual private networks (VPNs).
Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN)
VXLAN is responsible for creating a virtual network for communication
between virtual machines.
It supports scalable network architecture,
and efficient operation in virtual machine and container-based
environments.
Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation (GENEVE)
GENEVE is used as an encapsulation protocol for communication in
virtualized network environments.
By providing a flexible header format, it can respond to a variety of
network environments and services.
It also provides features such as tunneling, virtualization, and
multi-protocol support to respond to network diversity and complexity.
AIWAF-VE and Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
As previously mentioned,
the primary purpose of integrating the Virtual Appliance security solution
with AWS GWLB is
to identify client IPs and enforce security policies.
In a configuration that goes through a load balancer operating as a proxy,
the source IP of traffic is changed to the IP of the load balancer.
Let's look at a few examples of what could happen
if only the same client IP (load balancer IP) is injected into the WAF (Web
Application Firewall) solution in this configuration.
Threshold policies based on IP are not available.
Additionally, exception handling becomes impossible due to having a trusted IP list.
Of course, you can use a session (Cookie) or fingerprint as a client
identifier to replace IP,
but it consumes a lot of system resources, and IP is still mainly used as
the basis for many solutions or operating policies..
MONITORAPP's AIWAF-VE
MONITORAPP's AIWAF-VE is fully integrated with AWS GWLB.
Deployed as a transparent proxy in a cloud environment,
it performs decapsulation and encapsulation for the GENEVE protocol,
and also supports encapsulation protocols such as GRE and VXLAN, which are
protocols for similar purposes.
All security policies and logging are processed in a decapsulated state,
allowing all security and convenience features provided in the existing
in-line operation mode to be used in the AWS GWLB environment.
If you would like to know more about AIWAF-VE, you can check it out through the link below.
https://www.monitorapp.com/ko/waf-ve-kr/
https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/prodview-aile4raij6obc


