
Weekly web attack trends
Weekly web attack trends allow you to see when web attacks are most prevalent. This can help you plan ahead to prevent and respond to web attacks during peak periods.
The graph below shows the web attacks detected by AIWAF as of January 2025.
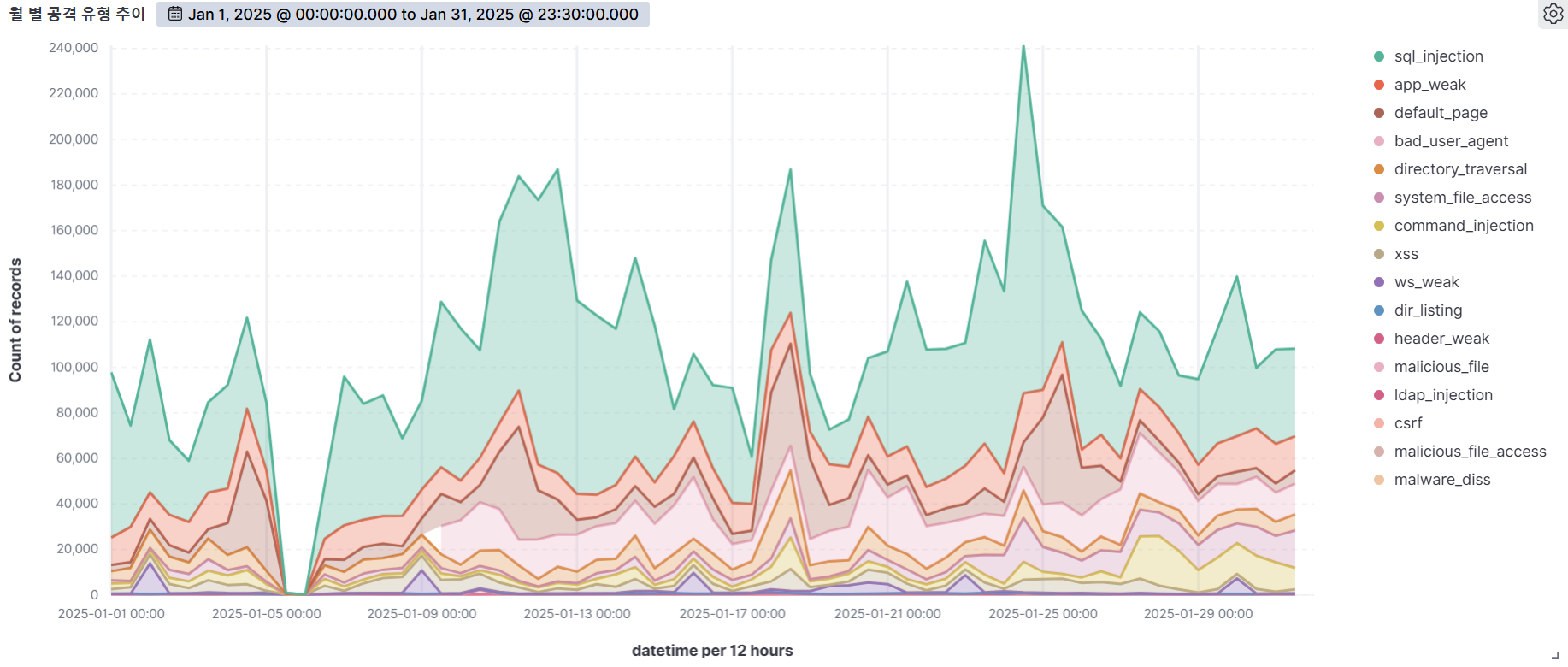
In January 2025, we detected an average of about 220,000+ attacks per day, with the highest number of attacks occurring on the 28th and 30th.
SQL Injection, the vulnerability with the most attempted attacks on the 24th, has the most detection conditions in our AIWAF. However, SQL Injection attacks are always being monitored because there are many new attack types and circumvention methods.
Web attack trends by attack type
Web attack trends by attack type, based on detection logs, allow you to see which attacks were most prevalent during the month. Based on this, you can establish basic web attack response guidelines to prevent and respond to these types of attacks.
The graph below shows the web attacks detected by AIWAF as of January 2025.
Web Attack Trends by Rule
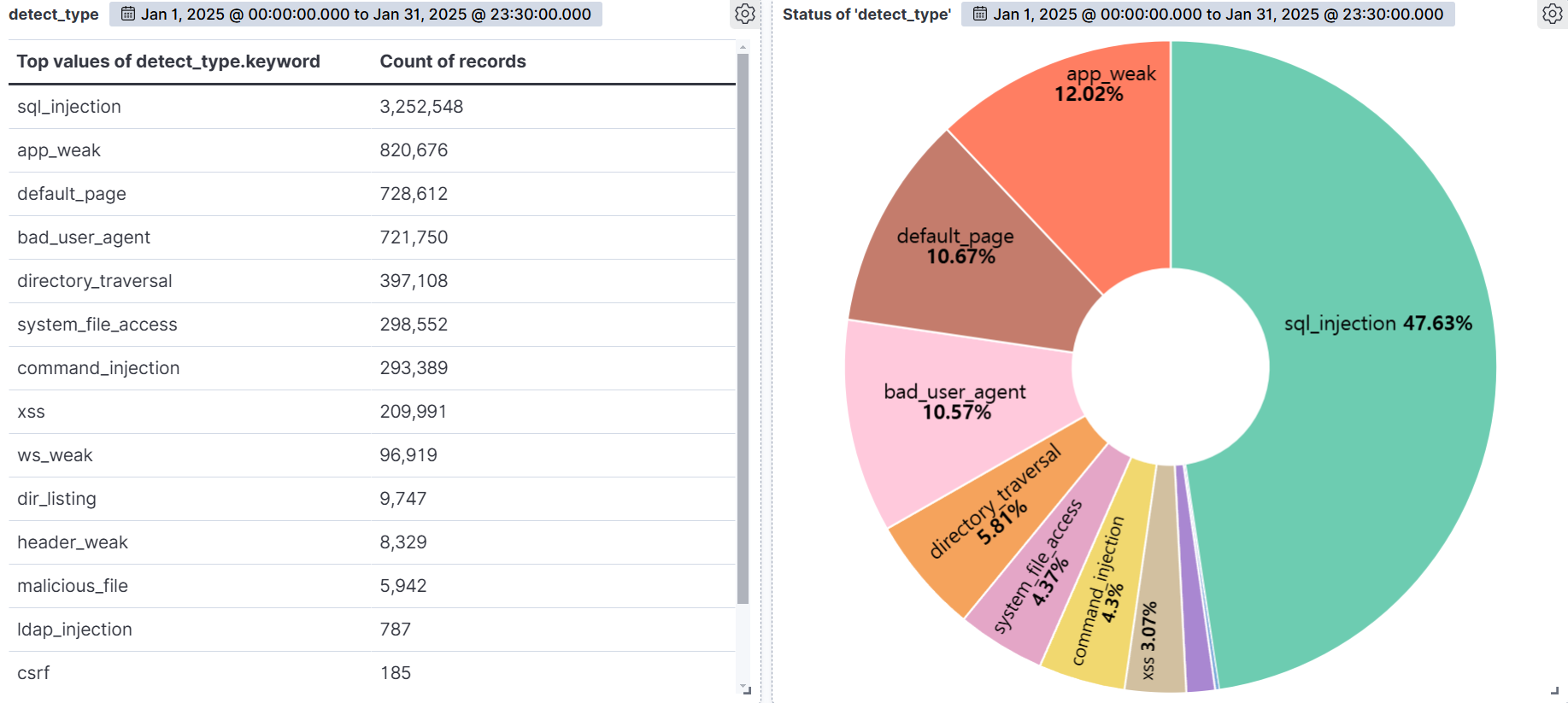
SQL Injection (47.63%) was the most common attack type, followed by App weak (12.02%), Default page (10.67%), and bad user agent (10.57%).
SQL Injection is the most diverse and dangerous attack, as it is ranked #1 by OWASP. It is an attack that forces malicious SQL statements into SQL syntax that dynamically generates data based on user requests, which can cause vulnerable applications to authenticate or return abnormal SQL results. If you encounter the following syntax in your query values, you should suspect an attack.
APP WEAK indicates a vulnerability within an app that an attacker can exploit to gain unauthorized access or perform malicious actions. These vulnerabilities can be the result of poor coding practices, misconfiguration, or insufficient security measures. As a general rule of thumb, be suspicious of unauthorized files in addition to authorized files when using app programs.
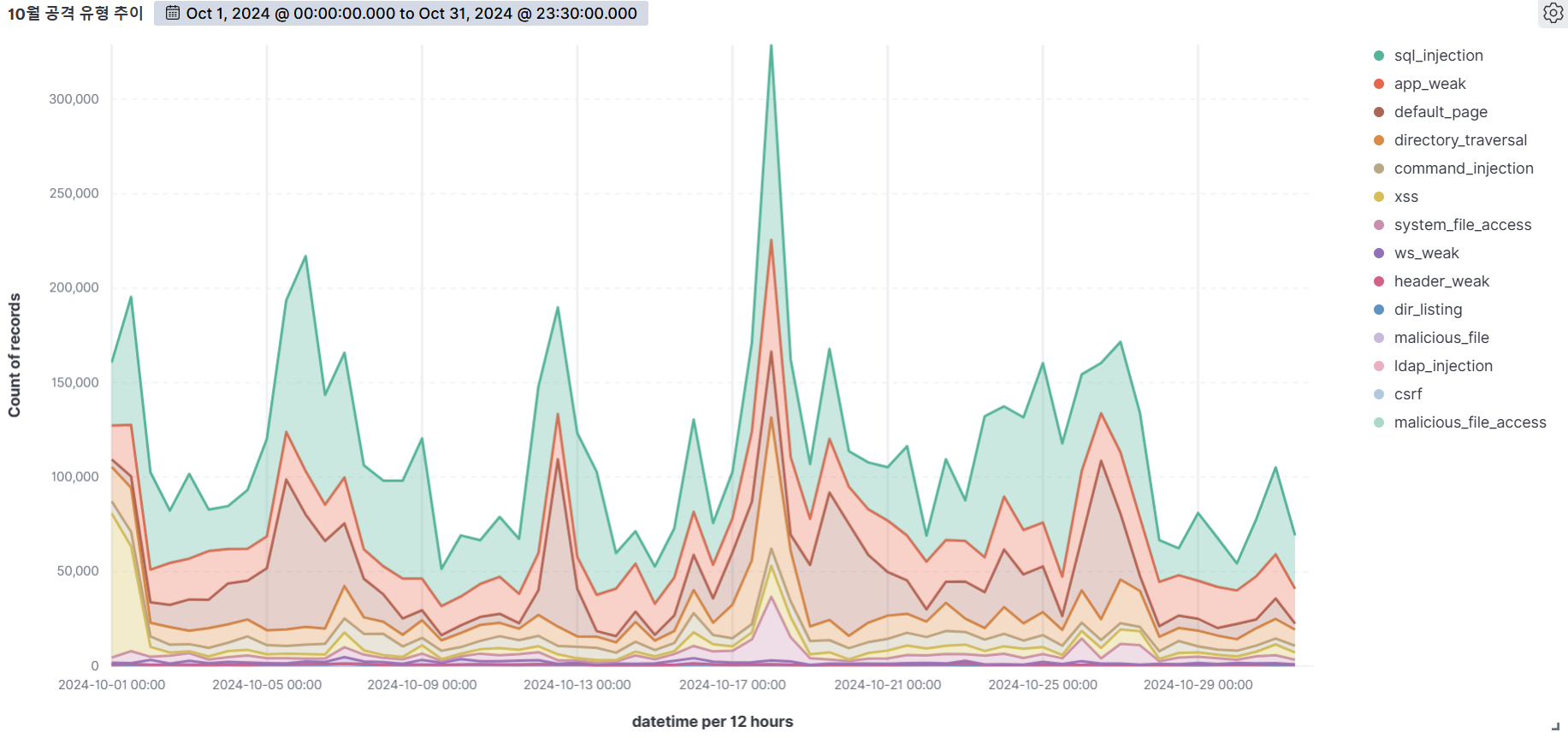
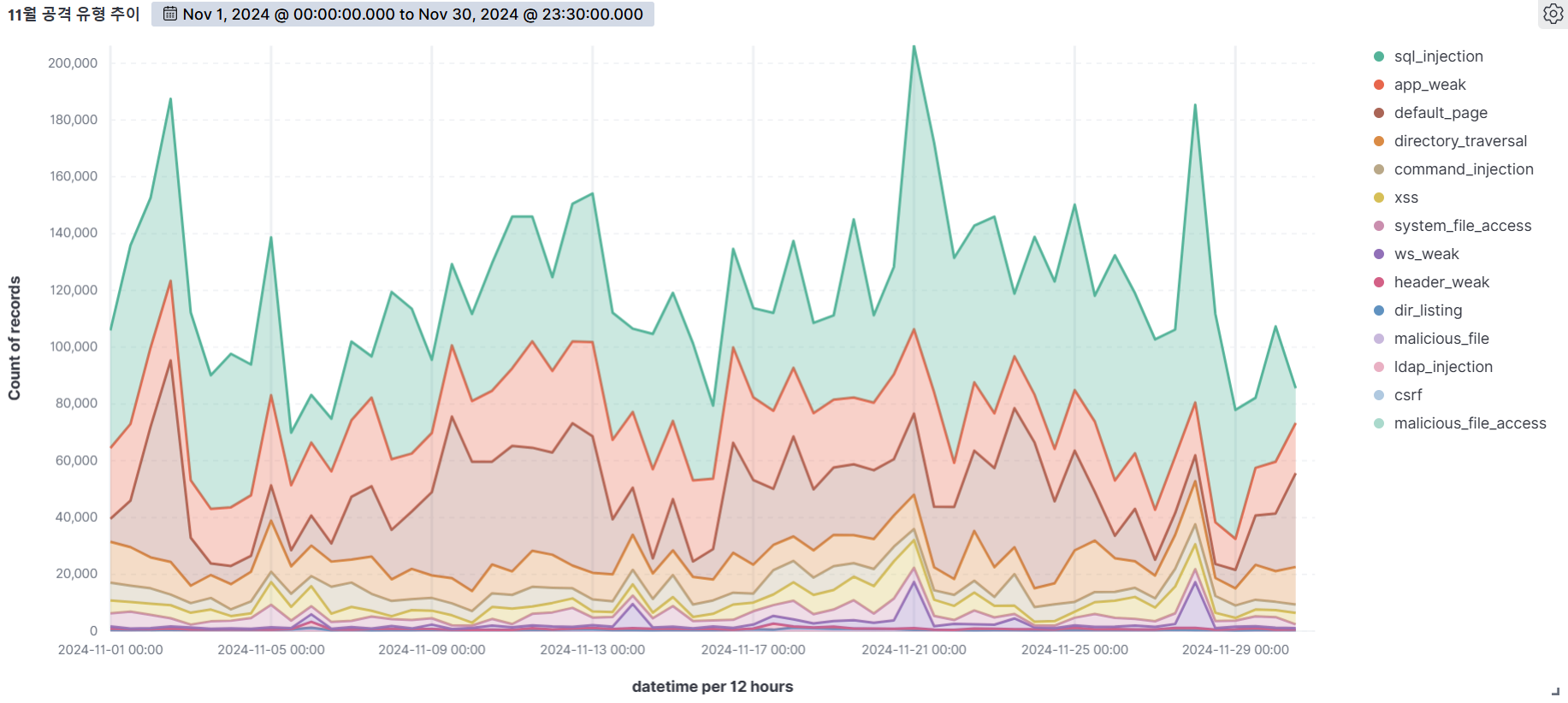
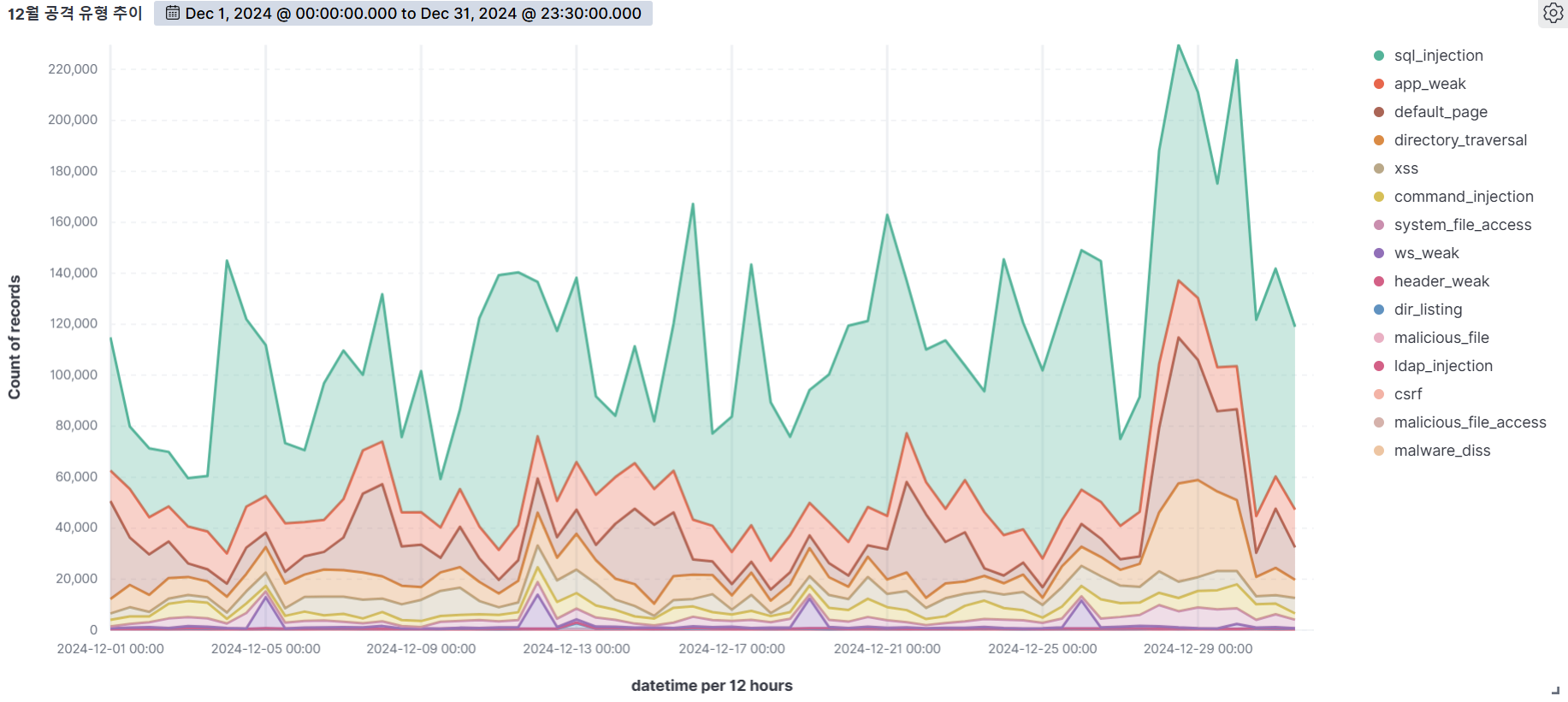
Summary of web attack trend graphs for the last 3 months
October
November
December
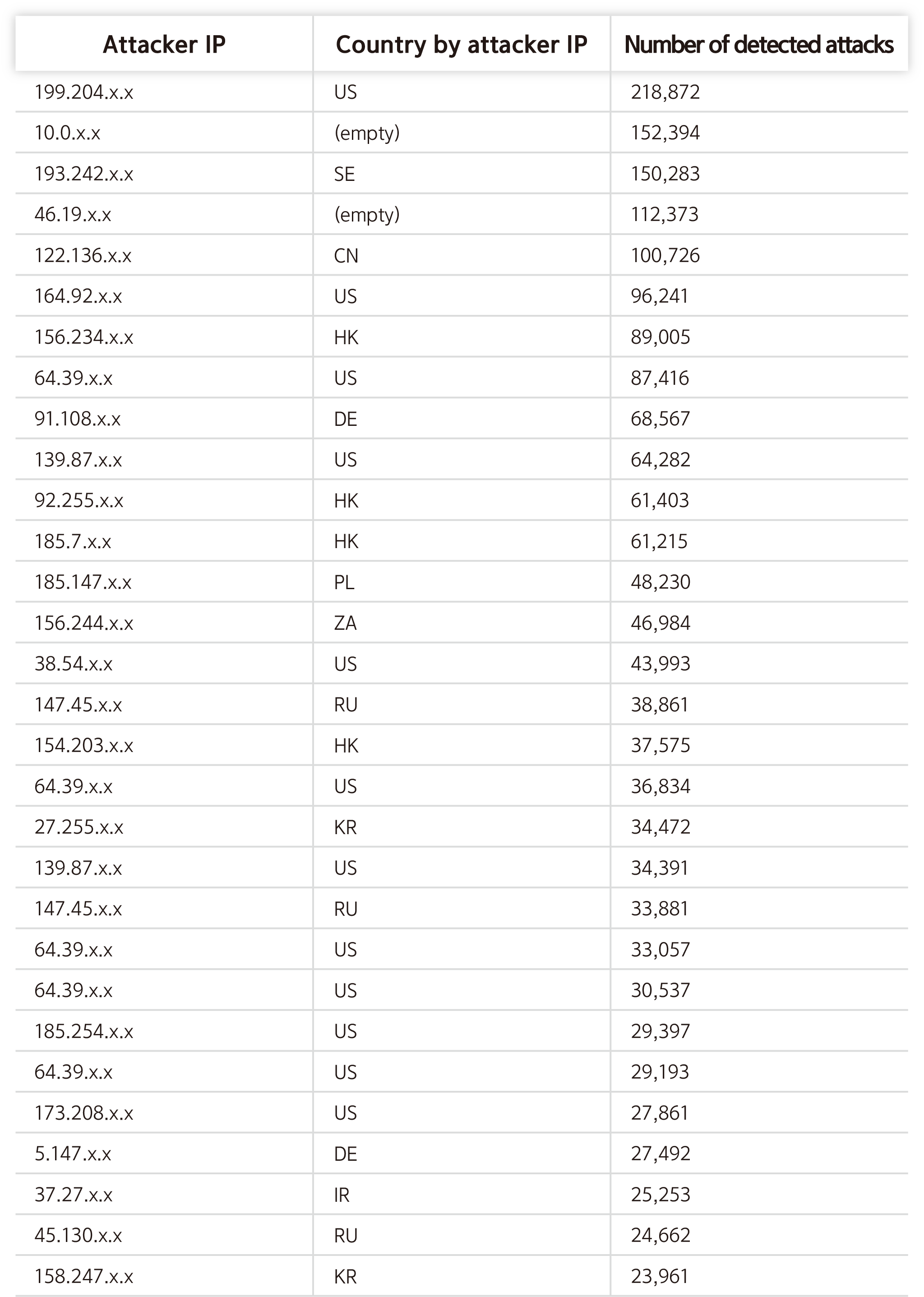
Top 30 Attacker IPs

Vulnerability analysis reports
Ivanti Connect Secure & Policy Secure, ZTA Gateways Vulnerability
1. Overview
Ivanti's Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways, a line of SSL VPN solutions and IPS solutions, recently published an analysis of CVE-2025-0282, a Buffer Overflow-based pre-authentication RCE vulnerability discovered in their platforms.

Source : https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2025/01/08/ivanti-exploited-connect-secure-zero-day-cve-2025-0282-cve-2025-0283/
2. Attack types
CVE-2025-0282 is a pre-certification RCE vulnerability in Ivanti's Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways products that allows an RCE attack by exploiting a buffer overflow in the IF-T/TLS protocol communication used by OpenConnect, an open source VPN client used by these products.
According to watchtowr, who analyzed the vulnerability, a portion of the code responsible for communicating with the protocol is incorrectly written to copy the size of the input string, rather than the size of the buffer, when using the strncpy function against the clientCapabilities variable, resulting in a BOF if more than 256 bytes of characters are entered.
Some of the code that watchtowr analyzed as vulnerable :

An attacker can utilize this part to attempt an RCE attack by first sending a GET request to make an IF-T/TLS request, and then proceeding with socket communication according to the protocol specification.
IF-T/TLS protocol communication requests :

Subsequent socket requests you send :

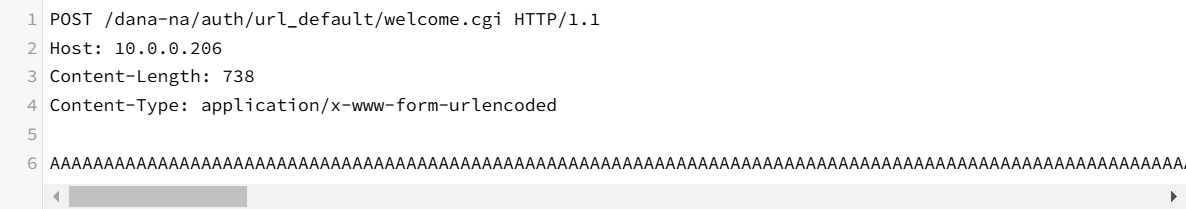
Alternatively, there are attacks that combine Webshell syntax with syntax that causes a buffer overflow and send it in a POST request.
Uploading BOF and Webshell via POST requests :
3. What to do
While Ivanti has released a patch for CVE-2025-0282, Ivanti Connect Secure and Ivanti ZTA Gateways products can be updated to version 22.7R2.5 or later to address the vulnerability, Ivanti Policy Secure products have not yet been patched and should follow Ivanti's recommended guidelines to avoid exposure to the Internet.
For this vulnerability, attacks occurring in the IF-T/TLS protocol environment do not appear to be covered by the AIWAF pattern, but attacks in combination with Webshell are mostly being detected by the “Webshell” pattern.
4. Conclusion
Over the last year and continuing this year, various vulnerabilities have been discovered and reported against Ivanti's products and solutions, some of which have been identified as more dangerous than others due to their ability to perform RCE attacks without authentication, and require quick updates to the latest versions.
In our AIWAF products, we have developed patterns to respond to vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways, and will continue to respond quickly to related vulnerabilities as they are discovered.
5. References
https://github.com/sfewer-r7/CVE-2025-0282
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/ivanti-connect-secure-vpn-zero-day
https://github.com/absholi7ly/CVE-2025-0282-Ivanti-exploit
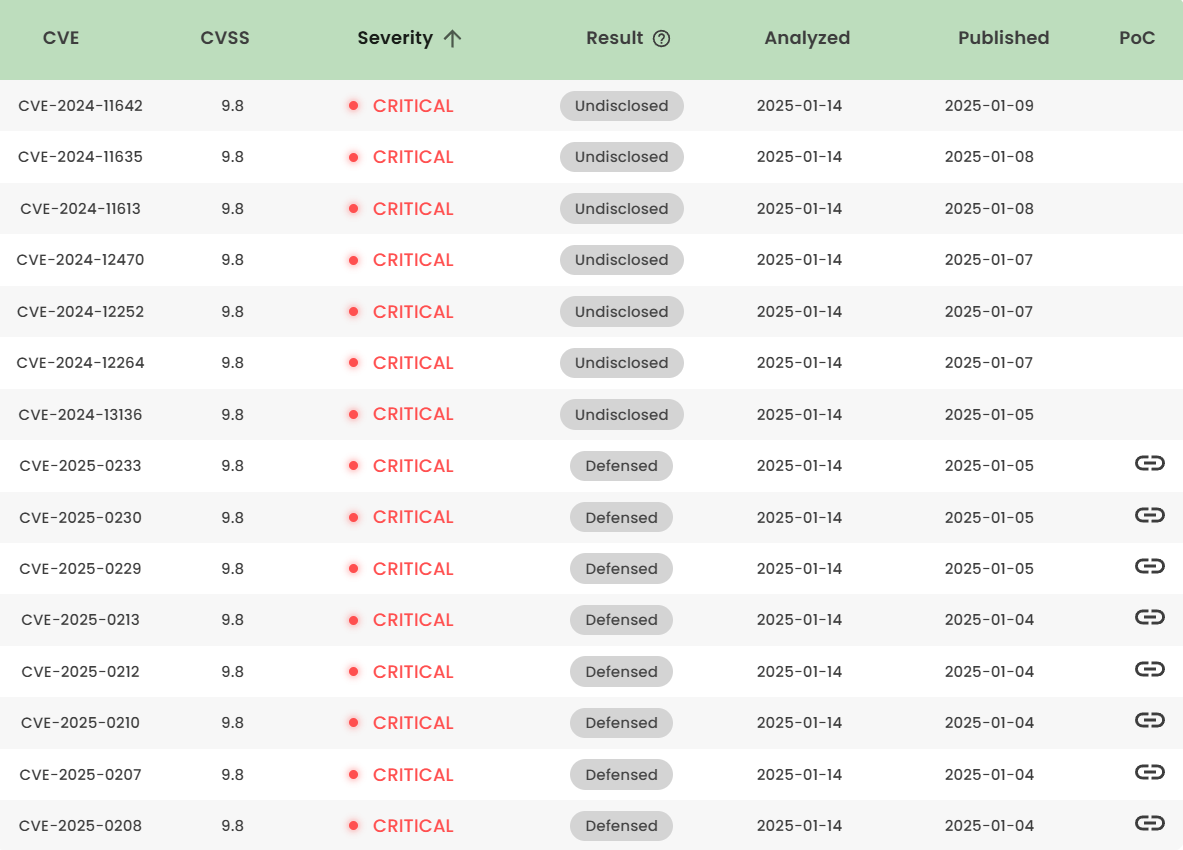
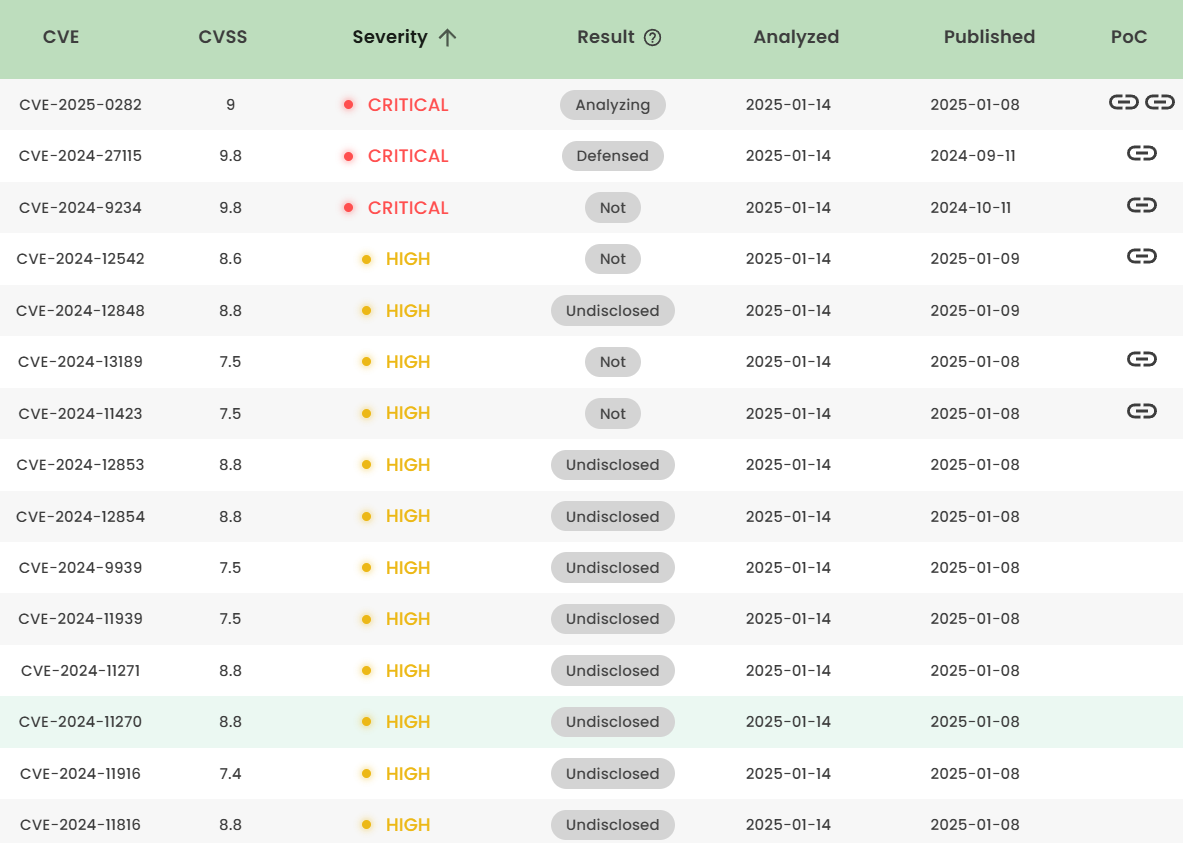
Latest vulnerability CVE status
1. High-risk vulnerability status (2025.01)
2. High-risk vulnerability descriptions



